Hello! I’m back after two-month hiatus. Did you miss me?
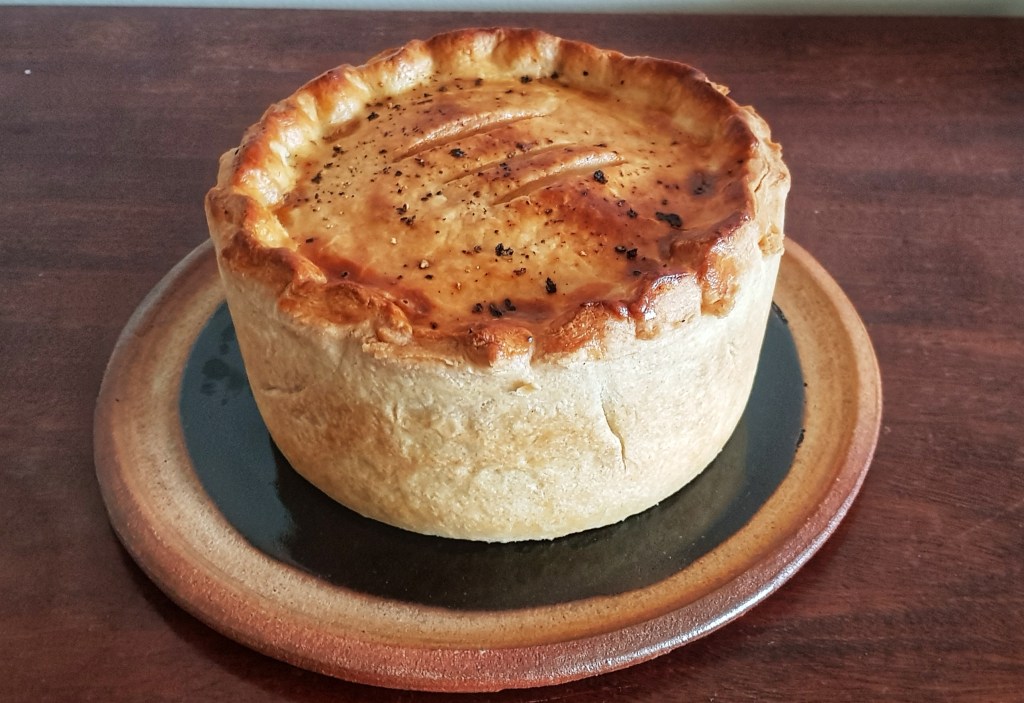
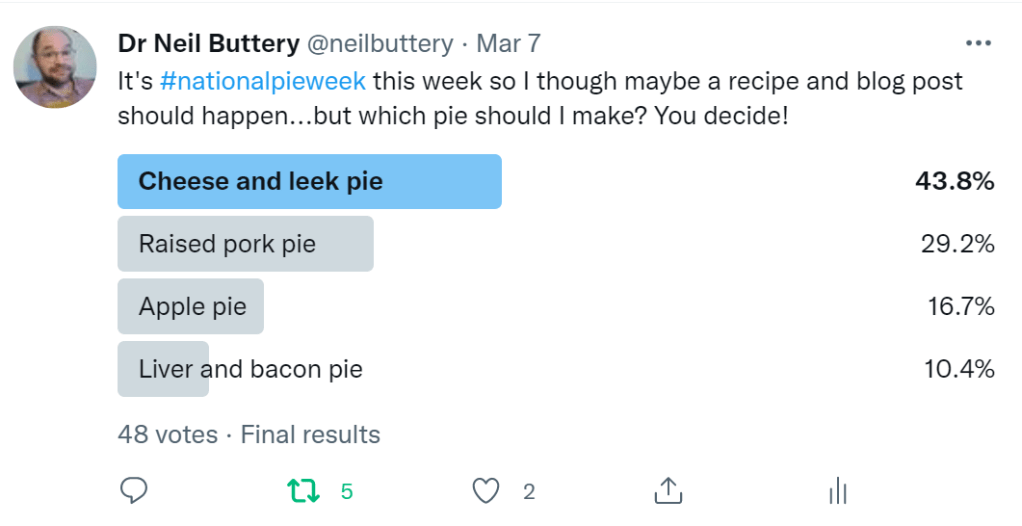
It’s British Pie Week this week so I thought I’d post a recipe for a favourite of mine. The trouble is, I have many favourites, so I came up with a list of four and let Twitter decide. I was very glad to see my favourite won.
Later, I saw the cheese and leek/onion pie was tenth in the top ten favourite UK pies, receiving just 1% of the vote!* Shocking. I think there may be a north-south divide effect at work there; back in the days of my market stall and restaurant, cheese and leek pie was by far the favourite.
The cheese and onion pie or pasty used to be a very important food for the working classes of Northern England, especially Yorkshire and Lancashire: it’s easy to make and the ingredients are cheap compared to meaty fillings. It’s the pie equivalent of the Welsh Rabbit/Rarebit.
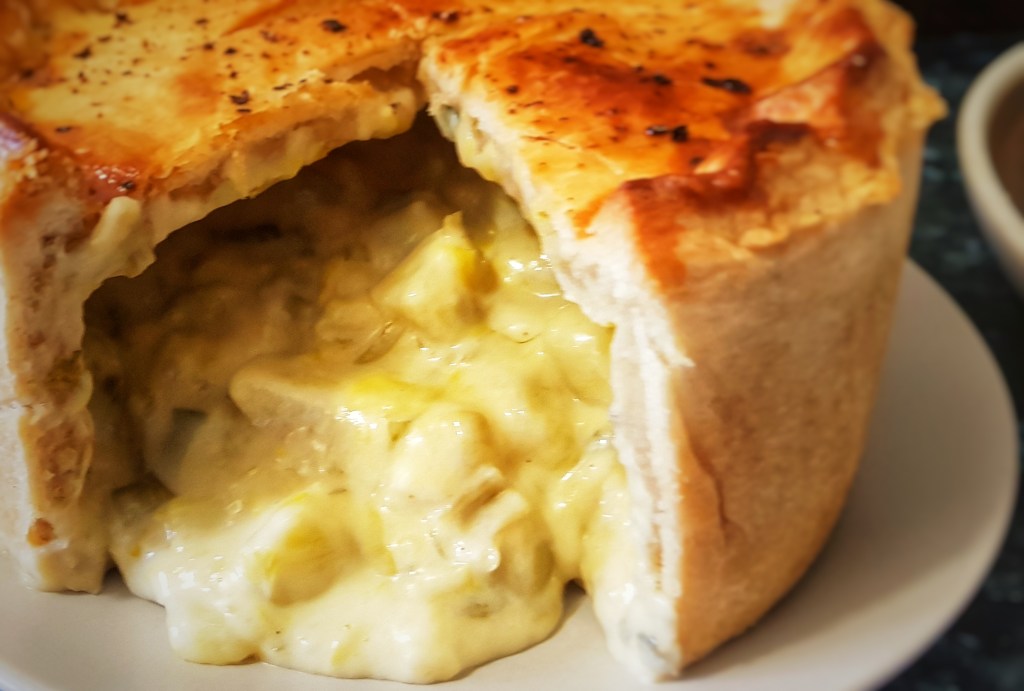
The simplest of fillings were made of cooked onion, thinly-sliced raw potato, or cold mashed potato, and grated cheese. On the fancier side, a thick white sauce is used instead of mash. For my recipe I am going somewhere in between to hopefully enjoy the best of both worlds. I use onion and leek interchangeably because either (or both) can be used: I make leek pies as I’m intolerant to onion.
As for the cheese, use a mature kind that melts easily: Cheddar, Lancashire, Double Gloucester etc. The pastry should be a simple shortcrust made with half butter, half lard, but all butter is good too.
Serve the pie with mashed potatoes or chips, with peas and gravy as is traditional, but this pie eats very well just warm with a dressed green salad and some good old salad cream.
If you like the blogs and podcast I produce, please consider treating me to a virtual coffee or pint, or even a £3 monthly subscription: follow this link for more information.
Makes one large pie to serve 6 people (or 4 greedy ones who always have seconds)
For the filling:
50 g butter
1 leek, trimmed and sliced, but with the green left on; or 2 medium onions, peeled and sliced
350 g (approx.) potatoes, peeled and diced (about 2 medium-sized ones)
Salt and pepper
1 tbs plain flour
1 tsp English mustard powder
275 ml hot milk
150 g grated cheese
Pinch Cayenne pepper (optional)
2 tbs double cream
For the pastry:
400 g plain flour
200g salted butter, or 100 g each butter and lard (or shortening)
120 ml water or milk
Egg wash
Start with the filling. Melt the butter in a saucepan and add the leek or onion and potatoes, season with half a teaspoon of salt and a good grind of pepper. Cook over a medium heat until the leek or onion melts right down. Do this slowly, turning down the heat if necessary – you don’t want to fry them, though a pale golden brown colour is fine.
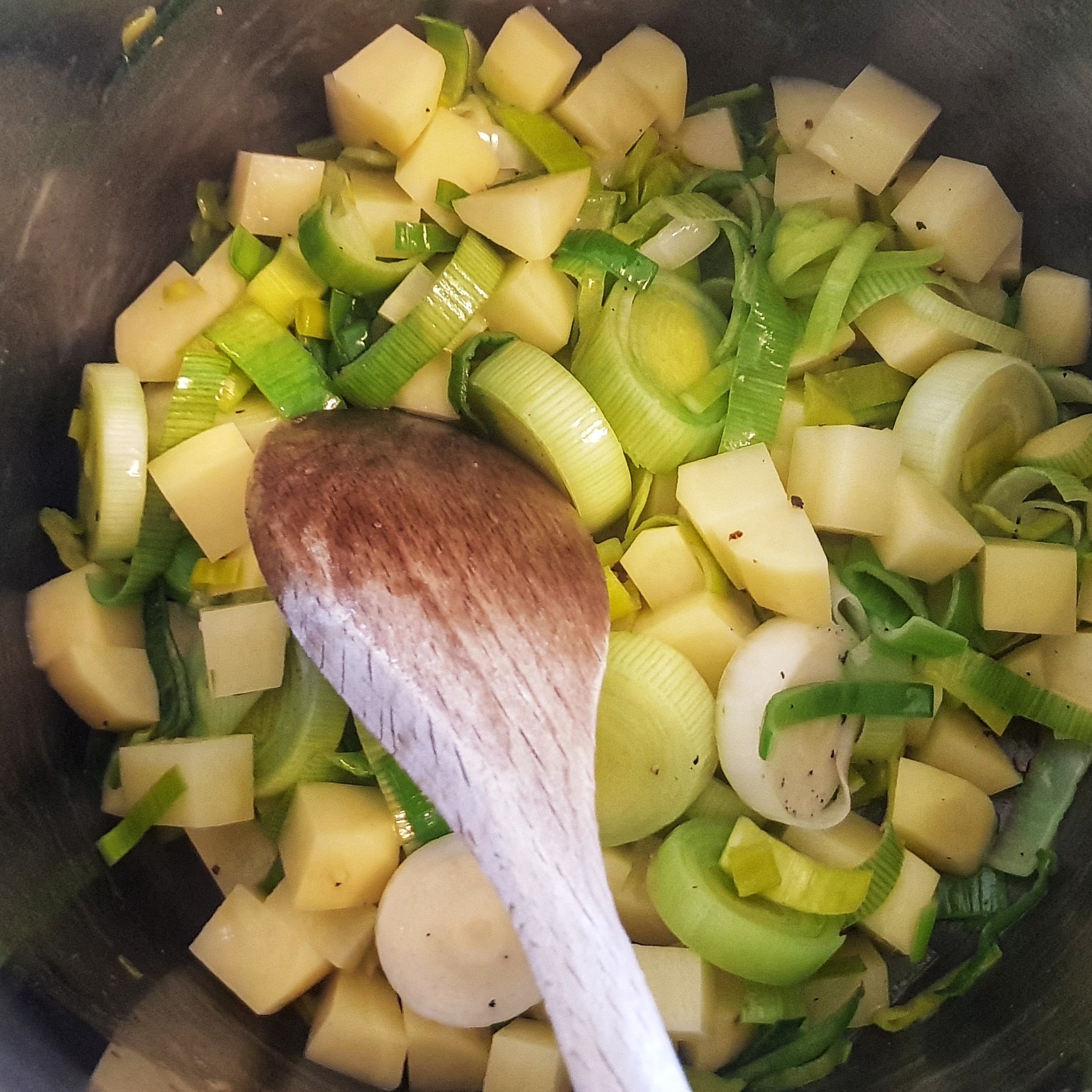
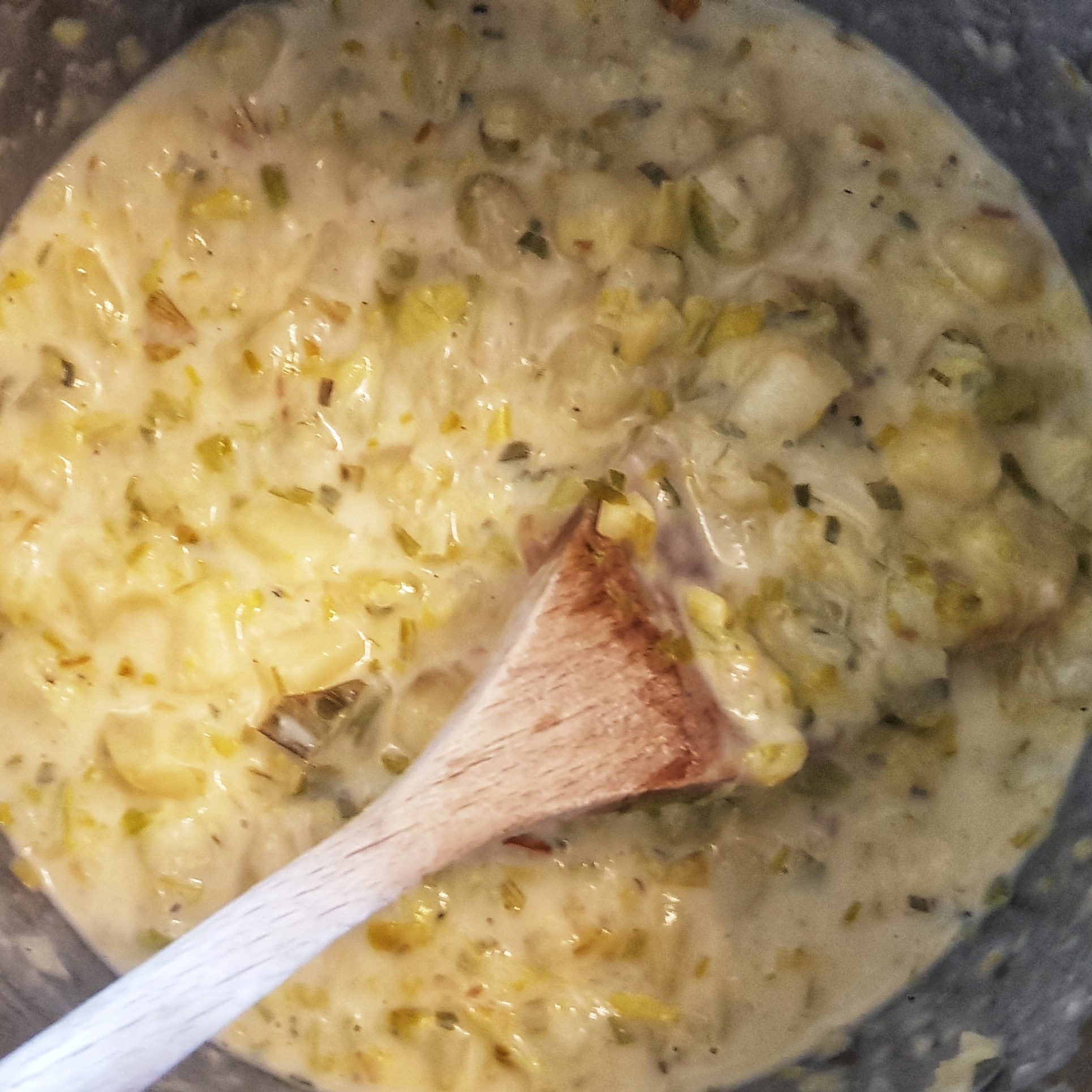


Stir in the flour and mustard and cook for a minute before mixing half of the milk. When the milk combines with the flour to make a smooth sauce, add the remainder of the milk and combine again.
Simmer gently for 10 minutes, stirring occasionally. Then remove from the heat and stir in the cheese. Mix in the Cayenne pepper. Check the seasoning and add more salt and pepper. It’s a good idea to slightly over season the filling to make up for the comparatively bland shortcrust pastry. Finally stir in the cream and allow to cool completely. I usually make my cooked fillings a day or two ahead of time.
Now make the pastry. Rub the fat(s) into the flour. If you are using unsalted butter, add half a teaspoon of salt. If you are making pastry by hand, unless you have forearms like Popeye, use fats that are at room temperature. If using a mixer, use the flat beater and use cold fats straight from the fridge. Either way, once it resembles breadcrumbs add the water a couple of tablespoons at a time until you have a soft but not sticky dough. Knead very briefly, wrap in cling film and leave it rest in the fridge for 30 minutes.
After resting, take around a third of the dough and roll out on a lightly floured worktop. I used an 18 cm cake tin because I like deep-filled pies, but a shallow pie dish or flan ring of around 25 cm would work too. Roll out a third of the pastry into a circle. Leave the pastry to rest again for a minute or so before laying it in the tin. Be careful to press the pastry into the corners without stretching it: lift it in carefully. If using a deep dish as I have it’s helpful to fold the pastry into quarters, placing it in the dish or tin and then unfolding it.
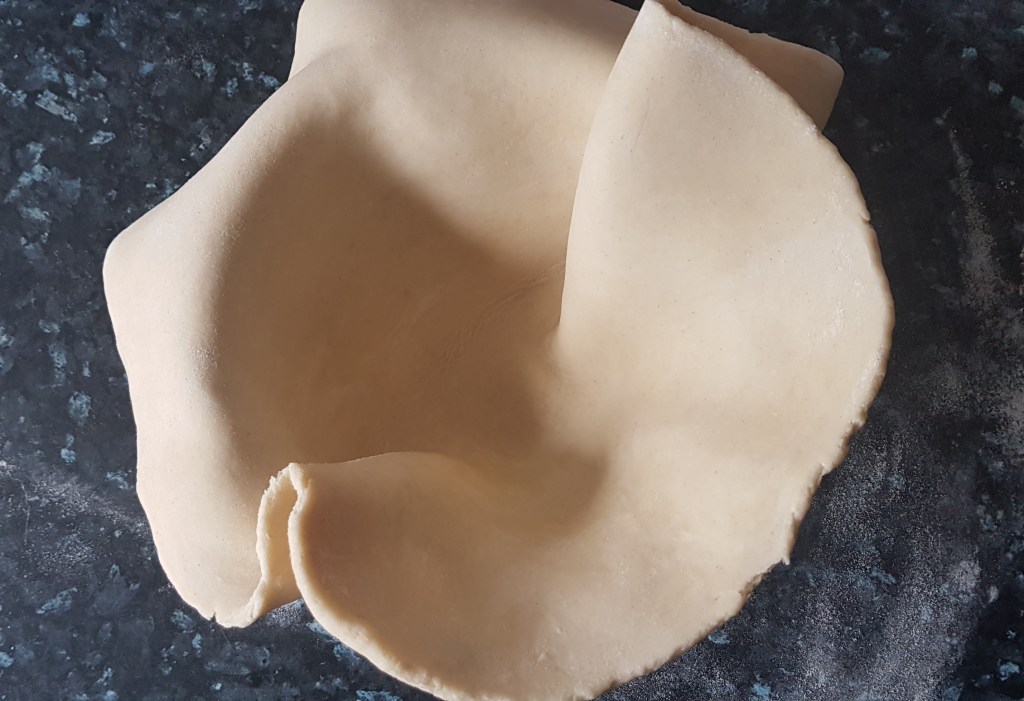
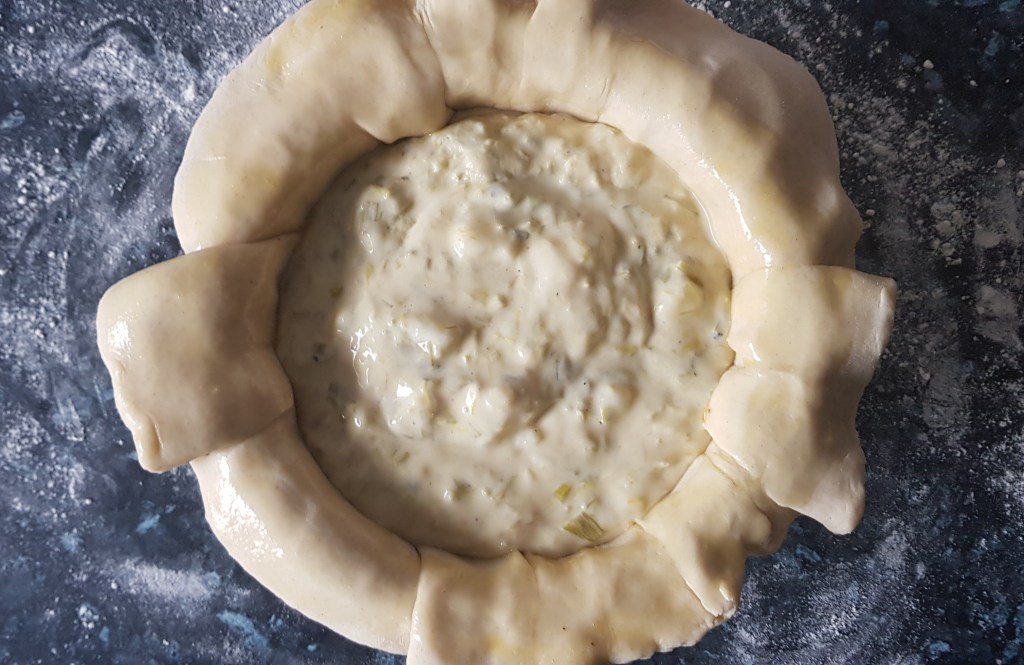
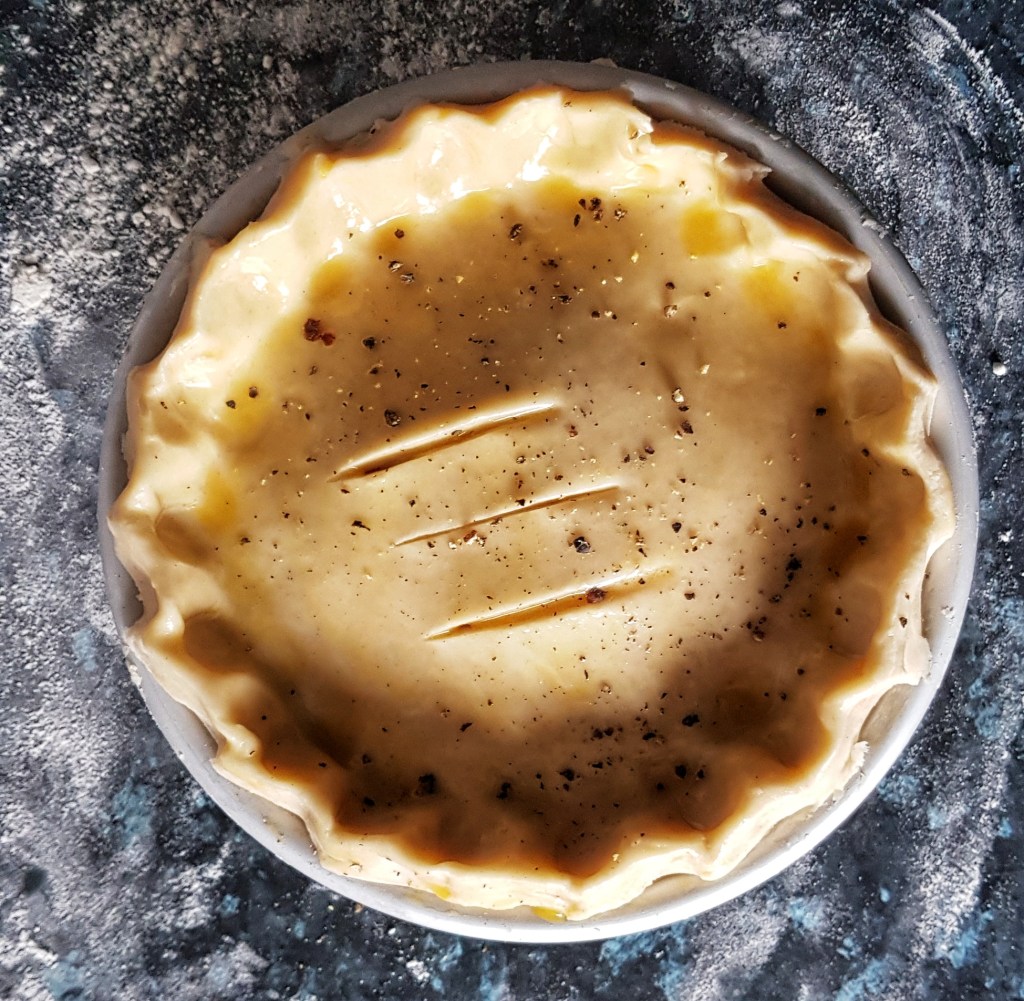




Roll out the remainder of the pastry to make a lid. Cut a steam hole in the centre and set aside.
Spoon in the pie filling, but don’t fill it too much – it does expand as it cooks. Now brush the edges with egg wash (I use an egg, or egg yolk, beaten with half a teaspoon of salt). Glue the lid in place, pressing the lid down well.
Trim the excess pastry with a sharp knife and then crimp the edges or use a fork to seal the lid. Paint with more egg wash, and if you like add a bit more black pepper. Place in the fridge to set the pastry.
Preheat your oven to 220°C and pop a baking tray on the centre shelf.
(If you have any left-over pastry and filling, make a pasty with it (see here for my Cornish pasty recipe) and bake it with the pie, or freeze it. Both pastry and filling freeze well separately.)
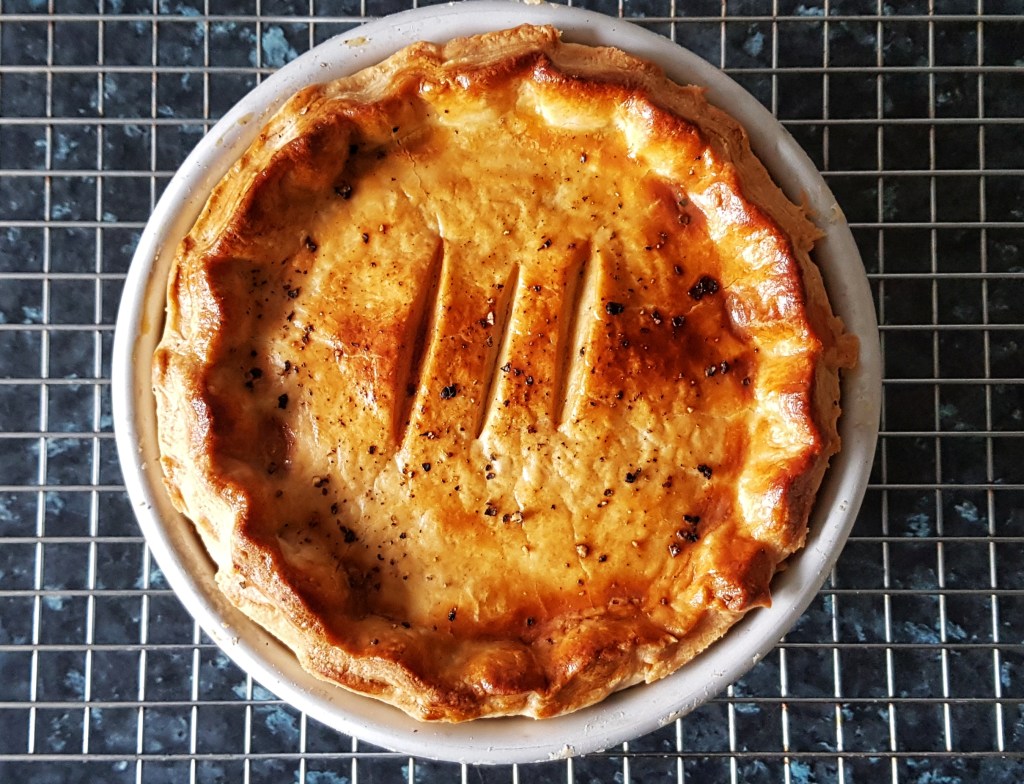
Take the pie out of the fridge and place in the oven on the hot baking tray (this prevents a soggy bottom from developing) and bake for 45 minutes, turning down the heat to 180°C when the pastry is a nice golden brown.
*The poll appeared in the Metro back in 2017: https://metro.co.uk/2017/03/09/the-most-loved-pies-around-the-uk-may-divide-the-nation-6498584/